In this post I am going to walk you through creating a virtual environment from the ground up to play with SQL Server 2012’s availability groups. In my opinion this feature alone is the number one reason to upgrade from previous SQL Server versions. When I say ground up I really do mean ground up we are going to create 4 VM’s a Domain Controller, 2 SQL Servers and a machine to run management studio (This is where our app that uses SQL Server would be) all running Windows Server 2012.
If you plan to follow along you will need the following
- SQL Server 2012 Enterprise ISO
- Windows Server 2012 Enterprise ISO
- VM software of some sort, I’m going to be using VirtualBox
It’s important to note there are many ways you can configure Availability Groups (auto failover, manual, read-only secondary, asynchronous commit, synchronous commit…). In this example I’m going to create an automatic failover group whereby the secondary node is queryable in read-only mode. This allows you to run reports/backups on this node keeping that load off the primary. In future posts I will go more in to the fail over side and the options for making secondary nodes take over when the primary goes offline.
As this is just a sandbox/tutorial I’m taking a couple of shortcuts namely I’m going to host the fail over cluster on the domain controller. Feel free to create a separate VM for this if you desire. I will also be creating some domain user accounts that are over powered so we can focus less on domain security and more on the SQL side of things.
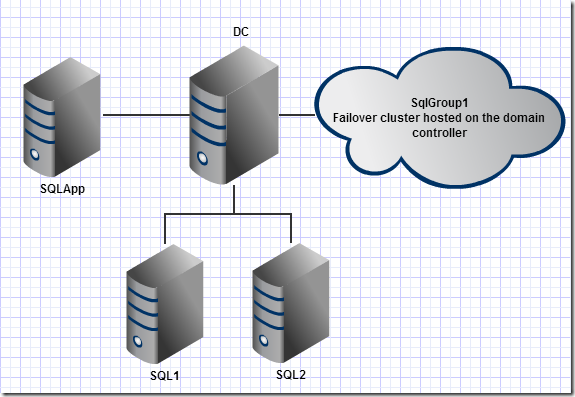
The network we will be creating is going to look like this…
SqlGroup1 is going to be the name of our failover cluster on the domain controller. This is what we will connect to for SQL access, this allows Windows Failover clustering to re-route our request should the primary server go down.
Create The VM’s
Create 4 VM’s naming them DC, SQL1, SQL2, SQLApp. Install Windows Server 2012 on each naming them the same as you named the VM. I went with 2GB of RAM for each and 25GB hard drives. You can give them bigger drives if you wish but that is enough capacity to build this sandbox. You will need to install Windows 2012 with it’s GUI to complete this guide, although everything here is possible from the command line I am not going to cover that.
This step is optional and will vary depending on which VM software you are using but I like to set all my VM’s to use an internal network so they can see each other but nothing else on the network. To do this in VirtualBox go to the settings for each VM and on the Network tab set the “Attached To” value of adapter 1 to “Internal Network”.
Configure Domain Controller
Static IP/DNS
- Right click the network icon by the clock in the bottom right and click “Open Network and Sharing Centre”
- Click “Change adapter settings”
- Right click Ethernet and click properties
- Click “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” then click properties
- Set the following manual addresses then click ok
IP : 192.168.10.1
Subnet mask : 255.255.255.0
Preferred DNS Server : 192.168.10.1
Add DNS/Domain Services Roles
- Open the “Server Manager” from the start screen
- Under “Configure this local server” click “Add roles and features”
- Click next until you get to the page when you need to pick which roles/features to add
- Tick the following 2 roles (make sure to also add the features for those roles when the popup appears)
- Active Directory Domain Services
- DNS Server
- Click next until you get to the install screen then click “Install”
- Once this has finished installing click “Close”
Promote to Domain Controller
- The “Server Manager” should now show an explanation mark next to the flag in the header bar, click on it
- Click “Promote this server to a domain controller”
- Select “Add a new forest”
- Enter “sql.sandbox.net” as the “Root domain name” and click next
- Enter a password and then click next/install right the way through
Users
- Open “Active Directory Uses and Computers” from the start screen
- Add the following new user to sql.sandbox.net/Users (Make a note of the password you choose) : admin
- Right click the new admin user and click “Add to group”.
- Enter “Domain Admins” and click “OK”.
- Add another user called “sqlacc”, don’t worry about making it a domain admin this is the user we will run the SQL Server service account under.
Join VM’s to domain
The following needs to be performed on SQL1, SQL2 and SQLApp. Log in to each server with the local admin account you created when you installed the VM. Then do the following
Static IP/DNS
- Right click the network icon by the clock in the bottom right and click “Open Network and Sharing Centre”
- Click “Change adapter settings”
- Right click Ethernet and click properties
- Click “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” then click properties
- Set the following manual addresses then click ok
IP : 192.168.10.x (Where x is 2 for SQL1, 3:SQL2, 4:SqlApp)
Subnet mask : 255.255.255.0
Preferred DNS Server : 192.168.10.1
Domain
- Press “Windows Key + Pause/Break”
- Under “Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings” click “Change settings”
- Click the “Change” button
- Change the computer name to match the VM name
- Select the domain radio button
- Enter the following domain “sql.sanbox.net”
- Click “OK”
- Enter the credentials for the domain admin account you created.
- Once the machine has restarted test that you can log in with the domain admin account you created ([email protected]).
Configure Failover Cluster
Installation
On the following Virtual Machines DC, SQL1, SQL2 do the following
- Open “Server Manager” from the start screen
- Under “Configure This Local Server” click “Add roles and features”
- Click next until you get to the features list
- Tick “Failover Clustering”
- Click “Add features”
- Click Next
- Click Install
- Once the installation has finished click Close
Configuration
On the DC virtual machine….
- Make sure you are logged in with the domain admin account you created
- Open “Fail over cluster manager” from the start screen
- Click “Create Cluster” on the right
- Click Next
- Add SQL1 and SQL2 to the server list
- Click next/finish until you get to the screen that asks for a cluster name
- Enter “SqlCluster” into the cluster name box
- Enter “192.168.10.5” into the address box
- Click next/finish right the way through
Install SQL Server
You need to install .Net 3.5 on SQL1, SQL2 and SQLApp before we can install SQL. It can be installed from features under “Add roles or features” in the Server Manager. On the confirmation tab you will need to specify an alternate source as if you’ve followed along the VM will not have internet access. Remount the Windows Server ISO and specify the alternate source as “D:\Sources\Sxs”.
Log into SQL1 and SQL2 as domain admin and perform the following steps
- Install a new stand alone install of SQL Server 2012 Enterprise on SQL1 and SQL2.
- Under feature selection you only need to install “Database Engine Services”
- On “Database Engine Configuration” under SQL Server Administrators add the domain admin account you created.
- When asked what account to run SQL Server under enter [email protected].
- Once the install has finished open “SQL Server Configuration Manager” from the Start screen.
- Right click “SQL Server (MSSQLServer)” on the right and click properties
- On the “Always On” tab click the checkbox to enable it and click ok"
- Restart the MSSql service
Log into SQLApp and install SQL Server Management Studio. You can do this through the normal SQL installer by picking Add features to an existing instance and choosing to install Management Studio.
You should then be able to run Management Studio on SQLApp under the domain admin account to connect to SQL1 and SQL2. If these fail it’s most likely due to the firewall on the server. You can either create firewall rules for SQL server or just turn off the firewall on SQL1 and SQL2. Once both these are working check you can also connect to SQLCluster.
Create Databases/Configure Availability Group
On SQLApp connect to SQL1 in Management Studio and do the following….
- Create a new database called TestDB
- Create a table called “Table1” with a couple of fields
- Insert a few records into the new table Backup the new database like this
BACKUP DATABASE TestDb
TO DISK = N'c:\backups\TestDb.bak'
WITH FORMAT
GOThen copy the backup to SQL2 and run the following SQL on SQL2 to restore the database
RESTORE DATABASE TestDb
FROM DISK = N'C:\BackupPath\TestDb.bak'
WITH NORECOVERY
GOWe now need to create an endpoint for the availability group on SQL1 (Primary). Run this query on SQL1
CREATE ENDPOINT dbm_endpoint
STATE=STARTED
AS TCP (LISTENER_PORT=7022)
FOR DATABASE_MIRRORING (ROLE=ALL)
GOWe then need an endpoint on SQL2 (Secondary), to do this run the following query on SQL2
CREATE ENDPOINT dbm_endpoint
STATE=STARTED
AS TCP (LISTENER_PORT=5022)
FOR DATABASE_MIRRORING (ROLE=ALL)
GOYou then need to execute the following SQL on both servers to give the SQL service user permission to connect to the endpoints.
CREATE LOGIN [sql\sqlacc] FROM WINDOWS;
GO
GRANT CONNECT ON ENDPOINT::dbm_endpoint
TO [sql\sqlacc];
GOThe next step is to create the availability group on SQL1. To do that run this query on SQL1
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP AG1
FOR
DATABASE TestDb
REPLICA ON
'SQL1' WITH
(
ENDPOINT_URL = 'TCP://sql1.sql.sandbox.net:7022',
PRIMARY_ROLE ( ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = READ_WRITE),
SECONDARY_ROLE (ALLOW_CONNECTIONS=READ_ONLY),
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL
),
'SQL2' WITH
(
ENDPOINT_URL = 'TCP://sql2.sql.sandbox.net:5022',
PRIMARY_ROLE ( ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = READ_WRITE),
SECONDARY_ROLE (ALLOW_CONNECTIONS=READ_ONLY),
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL
);We then need to join SQL2 to this availability group by running the following query on SQL2
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG1 JOIN;
Lastly we need to join the secondary database on SQL2 to the group. To do this run the following statement on SQL2
ALTER DATABASE TestDb SET HADR AVAILABILITY GROUP = AG1;
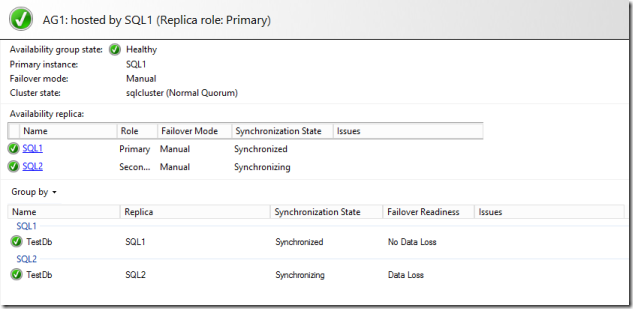
Availability Group Dashboard
If you connect to SQL1 in SQL Management studio and do the following you will be able to check the status of the availability group.
- Expand the availability groups node.
- Right click “AG1 (Primary)” and click show dashboard. </ol>
The dashboard should indicate the group is setup/synching and should look like this....
Demo
Right so now that is setup what can we do with it? For now let’s ignore the fail over side of things as I will cover that in a separate blog post. Lets just do a quick test to see the syncing in action and see how we now potentially have a read-only reporting server to off load some traffic from our main SQL instance.
Open 2 query windows and connect one to SQL1 and the other to SQL2. When you connect to SQL2 click options in the login dialog and under Additional Connection Parameters enter the following
ApplicationIntent=ReadOnly
Without this you will not be able to query the database on SQL2 as it is read-only. In each query window run the following query
SELECT * FROM Table1
You should get the same results from both as they have come from the same backup. Now in the query window for SQL1 insert some more records. If you then run both your select queries you will see the data has been synced to both servers. If you want to test SQL2 is actually read-only try to run an insert in the SQL2 query and you will see it fail.
I imagine you will already see how useful this is for scaling read-only traffic on multiple databases out to secondary instances. I will go into detail on the failover side of this in a future post as there is still a lot of ground to cover and I’ve gone on for way too long already.